01 Pages : 1-17
Abstrict
To determine the frequency of iron deficiency anemia (IDA) in children who present with clinical pallor The study was conducted at a tertiary care hospital, Hayatabad Medical Complex, between August 2018 and July 2022. We utilized laboratory information and took blood samples of 5ml to check for hemoglobin and ferritin levels. The criteria for IDA diagnosis were the presence of low hemoglobin levels (<11gm/dl) and low ferritin levels (<30ng/ml). The data were analyzed using SPSS version 26. The study contained 492 children between the ages of 1 year to 15 years. The total number of anemic was 467 (94.9%) and Iron Deficiency Anemia was found to be present in 28.8% of the patients. Our study concludes that the frequency of iron deficiency is high in children presenting with pallor. Initiatives like National programs incorporating short-term measures like iron supplements and long-term ones like fortifying wheat flour could decrease the burden of IDA.
Keywords
Iron Deficiency Anemia, Pallor, Children, Prevalence
Introduction
A disease is a particular abnormal condition, a disorder of a structure or function that affects part or all of an organism. Pulmonary tuberculosis is a contagious bacterial infection that affects the lungs. Pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) is caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It can be spread through breathing in air droplets from a cough or sneeze of an infected person. Once exposed to the infection, the patient may either have an active or latent infection. In active infection patient has signs and symptoms produced by actively replicating tubercle bacilli. In the case of pulmonary TB, the patient is potentially contagious and has symptoms like cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, weight loss, fever, and night sweats. Those having latent infection are not infectious and do not show symptoms or signs of TB, but they are at risk of developing active TB during their lifetime. The time during the exposure to Mycobacterium tuberculosis and the development of active infection is called the incubation period. It may vary from a few months to a few years. (Walker & Whittlesea, 2007c) Pakistan ranks 5th globally among the 22 high-burden tuberculosis countries, contributing 43 percent of the disease in the Eastern Mediterranean region of the World Health Organization (Programme, 2011b). Annually around 43,000 people including 15,000 children contract TB in Pakistan while not less than 70,000 deaths every year can be attributed to the disease in the country. TB is a leading infectious cause of death worldwide. Pakistan is also estimated to have the fourth highest prevalence of multi-drug resistant TB (MDR-TB) globally. Whereas globally 9.6 million fall ill and 1.5 million die due to TB every year. Over 95 percent of TB deaths occur in low and middle-income countries. (Programme, 2011)
The persons at high risk of active TB include the elderly, infants, and people with weakened immune systems, for example, due to AIDS, chemotherapy, diabetes, or medicines that weaken the immune system.
Signs and symptoms of having Pulmonary TB are cough (usually with mucus), coughing up blood, excessive sweating, especially at night, fatigue, fever, weight loss, breathing difficulty, chest pain, and wheezing. Lab tests are performed to diagnose Pulmonary TB i.e. CT-scan, Chest X-ray, Bronchoscopy, Sputum examination and culture test, Biopsy of the infected tissue, CBC, and Tuberculin skin test (PPD).
The goal of treatment is to cure the infection with drugs that fight the TB bacteria. Treatment of active pulmonary TB will always involve a combination of many drugs (usually four drugs). All of the drugs are continued until lab tests show which medicines work best. WHO guidelines are followed for the treatment of Pulmonary TB (see Annexure 2). Anti-TB medicines have been used for decades and sometimes strains are resistant to one or more of the medicines. Drug resistance emerges when anti-TB medicines are used inappropriately, through incorrect prescription by healthcare providers, poor quality drugs, and patients stopping treatment prematurely.
Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (TB) is a form of TB caused by bacteria that do not respond to isoniazid and rifampicin, the two most powerful, first-line anti-TB drugs. MDR-TB is treatable and curable by using second-line drugs (see Annexures 1 and 2). First-line agents used in the treatment of pulmonary TB are Isoniazid, Rifampin, Pyrazinamide, and Ethambutol. The second-line agents are also used in some patients. These are Amikacin, Ethionamide, Moxifloxacin, Para-aminosalicylic acid and Streptomycin. [American 2012]
Pharmacists play a vital role in the management of patients with TB by providing their expert approach to patient care. They can assess the appropriateness, efficacy, and safety of anti-TB therapy by monitoring patients and ensuring medication adherence. They can educate patients and clinicians about the expected therapy outcomes and the side effects as well as drug interactions associated with anti-TB agents. Minor adverse events such as gastrointestinal disturbances are common in the first few weeks of therapy and usually do not necessitate discontinuation of first-line agents. Patients may choose to take their medications with food, although absorption may be delayed. Other adverse events such as drug-induced hepatitis, pyrazinamide-induced hyperuricemia, and ethambutol-induced optical neuritis are more serious, require further evaluation, and may necessitate discontinuation of therapy. Pharmacists may recommend pyridoxine to decrease the risk of isoniazid-induced neuropathy. They should screen patients with comorbid conditions such as HIV infection for potential drug interactions, particularly those patients receiving rifamycin and protease inhibitors. Pharmacists can also educate patients about the importance of adherence and to ensure efficacy and minimize resistance. They should remain vigilant to avoid the addition of a single agent to a failing regimen. (Tavitian et al., 2003) In the light of above discussion, the following are the aims and objectives of the study:
1. To study the prevalence of pulmonary TB.
2. To study the prescribing trend in the management of pulmonary TB.
3. To assess any adverse drug effects related to anti-TB drug therapy.
4. To observe the laboratory test that is usually done for TB patients.
5. To study the role of pharmacists in the management of pulmonary TB to improve patient compliance.
Literature Review
Pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease that affects the lungs. It is caused by bacteria whose scientific name is Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It was first isolated in 1882 by a German physician named Robert Koch who received the Nobel Prize for this discovery. TB most commonly affects the lungs but also can involve almost any organ of the body. Many years ago, this disease was referred to as "consumption" because, without effective treatment, these patients often would waste away. Today, of course, tuberculosis usually can be treated successfully with antibiotics. (Troy & Beringer, 2006)
Tuberculosis (TB) is an important public health problem worldwide. In industrialized countries, the number of reported cases leveled out in the mid to late 1980s and then started increasing. This increase also occurred in countries across all countries, leading the World Health Organization (WHO) to declare tuberculosis a global emergency in 1993 (Walker & Whittlesea, 2007c).
Tuberculosis causes about 2 million deaths worldwide each year and one-third of the world's population is infected with the tubercle bacillus. It is becoming the leading cause of death among HIV – positive people. Globally over 3 million cases of tuberculosis diseases are notified annually although the estimated number of new cases is put at 8 million. The majority of cases occur in poor countries in the southern hemisphere, but TB is re-emerging in Eastern Europe, which experiences over a quarter of a million cases each year (Dye, 2006).
It is currently estimated that about one-third million people have active disease. Worldwide, 8 million new cases occur and 2 million people die of the disease each year. The figures don’t give the full picture because of under-reporting and under-recording in all countries (WHO, 2012).
Pakistan ranks 5th globally among the 22 burdened tuberculosis countries, contributing 43 percent of the disease in the Eastern Mediterranean region of the WHO. Annually around 43,000 people including 15,000 children contract TB in Pakistan while not less than 70,000 deaths every year can be attributed to the disease in the country (Tuberculosis, 2017).
Tuberculosis infection is caused by tubercle bacilli, which belong to the genus Mycobacterium. These form a large group, but only three relatives are obligatory parasites that can cause TB. They are part of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex and include M. tuberculosis, M. bovis, and M. africanum. However, the first two groups are 98% responsible.
The vast majority of other members of the genus Mycobacterium are saprotrophs and are widely distributed in the environment, often in soil, mud, and water. There is no evidence of person-to-person transmission. The initial infection may progress to pulmonary tuberculosis or, lymphohaematogenous spread of bacilli to pulmonary, meningial, or disseminated disease (military T.B). Infants, adolescents, and immunosuppressed people are more susceptible to TB or TB meningitis. Children have generally been considered to have a low risk of transmitting TB. They usually develop non-cavitary TB and frequently do not have a productive cough. However, children with TB have infected other individuals. Pulmonary tuberculosis is more common than extrapulmonary (non-respiratory) TB contenting for about 70% of cases in the UK (Fitzgerald et al., 2015).
Progressive pulmonary TB arises from exogenous reinfection or endogenous reactivation of a latent focus remaining from the initial infection. It may take many months from the time the infection initially gets into the lungs until symptoms develop. The usual symptoms that occur with an active TB infection are generalized tiredness or weakness, weight loss, fever, and night sweats. If the infection in the lung worsens, then further symptoms can include coughing, chest pain, coughing up of sputum (material from the lungs) and/or blood, and shortness of breath. If the infection spreads beyond the lungs, the symptoms will depend upon the organs involved (American, 2012).
Drug-resistant TB (TB that does not respond to drug treatment) has become a very serious problem in recent years in certain populations. Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) refers to organisms that are resistant to at least two of the first-line drugs, INH and Rifampin. More recently, extensively (extremely) drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB) has emerged. These bacteria are also resistant to three or more of the second-line treatment drugs. XDR-TB is seen throughout the world but is most frequently seen in the countries of the former Soviet Union and Asia. [Raviglione 2010]
Approximately 10% of all individuals infected with M. tuberculosis develop active disease (TB) sometime during their life. The risk of developing active TB is greatest in the first 2 years after initial infection. Re-infection can occur, although this is uncommon. The incubation period from infection to demonstrable primary lesion or significant tuberculin reaction ranges from 2 to 10 weeks. Latent infection may persist for a lifetime. HIV infection appears to shorten the interval for the development of clinical tuberculosis (Peloquin, 2011).
The risk of transmission of TB from one individual to another is dependent upon the patient with active infection, the environment, and the susceptibility of the exposed person. There is no strong evidence for a genetically determined (inherited) susceptibility to TB (Corbett, 2012).
TB can be diagnosed in several different ways, including chest X-rays, analysis of sputum, and skin tests. Sometimes, the chest X-rays can reveal evidence of active tuberculosis pneumonia. Other times, the X-rays may show scarring (fibrosis) or hardening (calcification) in the lungs, suggesting that the TB is contained and inactive. Several types of skin tests are used to screen for TB infection. These so-called tuberculin skin tests include the Tine test and the Mantoux test, also known as the PPD (purified protein derivative) test. In each of these tests, a small amount of purified extract from dead tuberculosis bacteria is injected under the skin. If a person is not infected with TB, then no reaction will occur at the site of the injection (a negative skin test). If a person is infected with tuberculosis, however, a raised and reddened area will occur around the site of the test injection. This reaction, a positive skin test, occurs about 48-72 hours after the injection. When only the skin test is positive, or evidence of prior TB is present on chest X-rays, the disease is referred to as "latent tuberculosis." This contrasts with active TB as described above, under symptoms. A special test to diagnose TB called the PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detects the genetic material of the bacteria. This test is extremely sensitive (it detects minute amounts of the bacteria) and specific (it detects only the TB bacteria). One can usually get results from the PCR test within a few days. [Manzurek 2010]
The goal of treatment is to cure the infection with drugs that fight the TB bacteria. Most regimens in the developed world now contain Isoniazid, Rifampicin, Pyrazinamide, and Ethambutol. In order to eradicate the bacteria in individuals, combination antituberculosis chemotherapy is always used. The choice of drug regimen is based on a number of factors, including a need to reduce the risk of resistance emerging and improve patient adherence (American, 2003).
A person with a positive skin test, a normal chest X-ray, and no symptoms most likely has only a few TB germs in an inactive state and is not contagious. Nevertheless, treatment with an antibiotic may be recommended for this person to prevent the TB from turning into an active infection. The antibiotic used for this purpose is called isoniazid (INH). If taken for six to 12 months, it will prevent the TB from becoming active in the future. In fact, if a person with a positive skin test does not take INH, there is a 5%-10% lifelong risk that the TB will become active (Ena & Valls, 2005).
Taking isoniazid can be inadvisable (contraindicated) during pregnancy or for those suffering from alcoholism or liver disease. Also, isoniazid can have side effects. The side effects occur infrequently, but a rash can develop, and the individual can feel tired or irritable. Liver damage from isoniazid is a rare occurrence and typically reverses once the drug is stopped. Very rarely, however, especially in older people, the liver damage (INH hepatitis) can even be fatal. It is important, therefore, for the doctor to monitor a patient's liver by periodically ordering blood tests called "liver function tests" during the course of INH therapy. Another side effect of INH is a decreased sensation in the extremities referred to as peripheral neuropathy. This can be avoided by taking vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), and this is often prescribed along with INH. (Jereb et al., 2011)
Active TB is treated with a combination of medications along with isoniazid. Rifampin (Rifadin), ethambutol (Myambutol), and pyrazinamide are the drugs commonly used to treat active TB in conjunction with isoniazid (INH). Four drugs are often taken for the first two months of therapy to help kill any potentially resistant strains of bacteria. Then the number is usually reduced to two drugs for the remainder of the treatment based on drug sensitivity testing that is usually available by this time in the course. Streptomycin, a drug that is given by injection, may be used as well, particularly when the disease is extensive and/or the patients do not take their oral medications reliably (termed "poor compliance"). Treatment usually lasts for many months and sometimes for years. Successful treatment of TB is dependent largely on the compliance of the patient. Indeed, the failure of a patient to take the medications as prescribed is the most important cause of failure to cure the TB infection. In some locations, the health department demands direct monitoring of patient compliance with therapy (Horne et al., 2006)
Surgery on the lungs may be indicated to help cure TB when medication has failed, but in this day and age, surgery for TB is unusual. Treatment with appropriate antibiotics will usually cure the TB. Without treatment, however, tuberculosis can be a lethal infection. Therefore, early diagnosis is important. Those individuals who have been exposed to a person with TB, or suspect that they have been, should be examined by a doctor for signs of TB and screened with a TB skin test (Cramer et al., 2008).
In pulmonary TB, sputum examination and culture are the most sensitive markers of the success of treatment. Patients taking regimens containing rifampicin and isoniazid should be non-infective within 2 weeks. If a patient does not become culture-negative, it may be due to either drug resistance or non-adherence, the latter being most likely. Chest radiographs provide only limited information as to the progress of treatment. Good adherence is essential if treatment is to successful, and checking adherence is not easy, especially when a patient is uncooperative. Rifampicin will color the urine red within about 4 hours of the dose and this has been used to monitor adherence (Cuneo & Snider, 1989).
The World Health Organization's recommended treatment strategy is to use a 'directly observed treatment short course' (DOTS). In this approach, health workers must watch their patients swallow each dose of drugs. This supervision must continue every day for the first 2 months and, ideally, for all 6 months of treatment (WHO, 2006).
Pharmacists play a vital role in the management of patients with TB by providing their expertise within an interdisciplinary team approach to patient care. Pharmacists can also educate patients about the importance of adherence and to ensure efficacy and minimize resistance. It should be emphasized that the disease will cured but this will take some months and the tablet needs to be taken as prescribed even if the patient feels better. Some patients will adhere later as they begin to feel better. A number of patients have a poor command of English. It may still be possible to give written instructions on dosage as some pharmaceutical companies are able to provide pictorial material and dosage sheets in a number of languages (Last & Kozakiewicz, 2009).
The occurrence of some adverse effects may require discontinuation of a drug, but others are harmless. The patient should be told which side effects to expect and which require referral to a number of health care teams. Again written instructions may be helpful. (Clark et al., 2007)
Patients taking rifampicin should be told that the drug will cause a harmless discoloration of their urine and other body fluids e.g. sweat and tears. The staining of tears is important if the patient uses soft contact lenses as these may be stained permanently. Gas permeable and hard lenses are unaffected, women using oral contraceptive pills should be advised to use other non-hormonal methods of contraception for the duration of treatment with rifampicin and for 8 weeks afterward. Although ocular side effects are rare when ethambutol is taken in normal dosages, patients should be warned of these potentially serious side effects. They should be advised to stop the drug and report to their doctor if they notice any changes in vision, such as a reduction in visual acuity or changes in color vision. This is especially important because visual changes are usually reversible on discontinuation of drugs but may be permanent if the drug is not stopped. Pharmacists should remain vigilant to avoid the addition of a single agent to a failing regimen (MMWR 2003).
Study Design
An observational and questionnaire survey-based study was conducted about the role of pharmacists in the Management Of Tuberculosis.
Sampling technique Random sampling
Inclusion Criteria Patients with Pulmonary T.B.
Exclusion Criteria Patients with Extra Pulmonary T.B.
Duration of Study 2 months (May-June)
Sample Size 50
Study Place Gulab Devi Chest Hospital, Lahore
Plan of Work A data collection form was designed and filled during face-to-face interviews with the patients and physicians.
Data was tabulated and presented in the form of graphs.
Results
Graphical Representation of Data
:The age group of patients:
Table 1
Sample size (N) = 50
|
Age |
Frequency |
% |
|
Below 30
years |
9 |
18 |
|
30 -60
years |
22 |
44 |
|
Above 60
years |
19 |
38 |
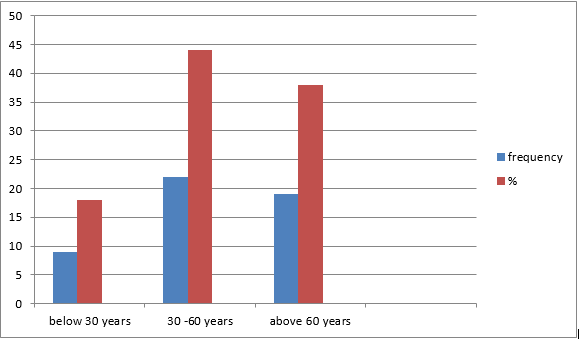
18% of
patients were below 30 years of age, 44% of patients were between 30-60 years,
and 38 % of patients were aged 60 and above.
§ Sex of
patients;
Table 2
Sample size (N) = 50
|
Sex of patients |
Frequency |
% |
|
Male |
30 |
60 |
|
Female |
20 |
40 |
Figure 2
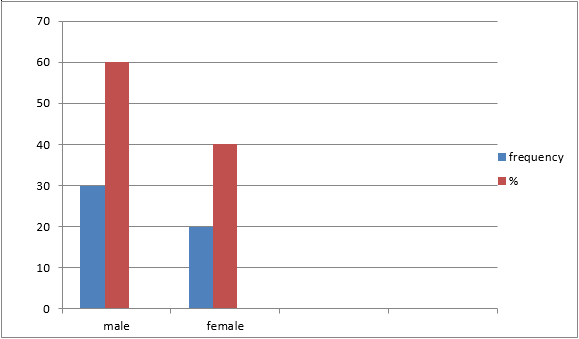
60 % of patients were male and 40% of patients were female.
§ Socioeconomic
status of patients:
Table 3
Sample size (N) = 50
|
Social status |
Frequency |
% |
|
Lower
class |
50 |
100 |
|
Middle
class |
0 |
0 |
|
Upper
class |
0 |
0 |
Figure 3
60 % of patients were male and 40% of patients were female.
§ Socioeconomic
status of patients:
Table 3
Sample size (N) = 50
|
Social status |
Frequency |
% |
|
Lower
class |
50 |
100 |
|
Middle
class |
0 |
0 |
|
Upper
class |
0 |
0 |
Figure 3
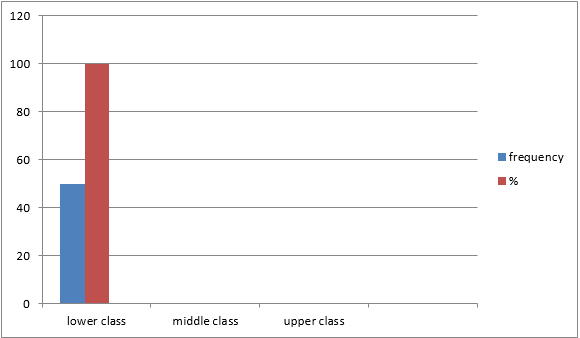
100% of pulmonary tuberculosis belonged to the lower class.
§ Adverse
effects experienced by patients after medications:
Table 4
Sample size (N) = 50
|
Status |
frequency |
% |
|
Yes
|
50 |
100 |
|
No |
0 |
0 |
Figure 4
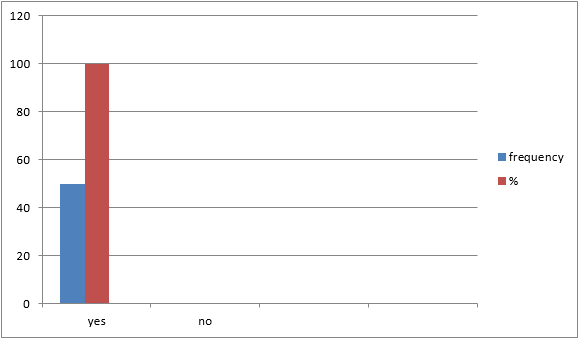
All the
patients experienced side effects after taking medications for pulmonary
tuberculosis.
§ Patient
compliance:
Table 5
Sample size (N) = 50
|
Status |
Frequency |
% |
|
Yes |
50 |
100 |
|
No |
0 |
0 |
Figure 5
.png)
100 % of patients were found compliant due to the DOTs
program.
§ Patients
used to smoke or weed drug addicts:
Table 6
Sample size (N) = 50
|
Status |
Frequency |
% |
|
Smokers/addicts |
14 |
28 |
|
Non-smokers |
36 |
72 |
Figure
.png)
28% of patients were found to be smokers and drug addicts
and 72% of patients were non-smokers.
§ Signs
and symptoms experienced by patients:
Table 7
Sample size (N) = 50
|
Sign and symptoms |
Frequency |
% |
|
Fever |
0 |
0 |
|
Cough |
3 |
6 |
|
Blood
sputum |
0 |
0 |
|
Dyspnea |
0 |
0 |
|
Body
pain |
0 |
0 |
|
Patients
with more than one symptoms |
47 |
94 |
Figure 7
.png)
6% of patients experienced productive cough and 94 % of
patients experienced more than one symptom.
§ Common
side effects reported by patients:
Table 8
Sample size (N) = 50
|
Side effects |
frequency |
% |
|
Nausea
|
5 |
10 |
|
Constipation
|
9 |
18 |
|
Dizziness
|
2 |
4 |
|
Urine
discoloration |
2 |
4 |
|
Cough |
1 |
2 |
|
Patients
with more than one side effects |
22 |
44 |
Figure 8
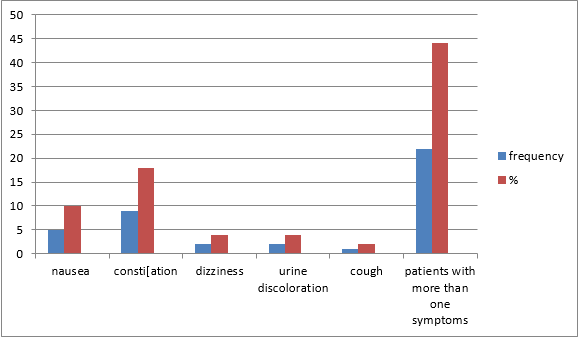
18% of the patients experienced dizziness as a side effect. Nausea, constipation, urine discoloration, and cough were also present in 10, 18, 4, and 2 patients respectively. 44 % of patients experienced more than one symptom.
Discussion
Tuberculosis (TB) is one of the major health problems in Pakistan. Pakistan ranks 5th amongst T.B. high-burden countries worldwide. It accounts for 61% of the TB burden in the WHO Eastern Mediterranean Region. Approximately 420,000 new TB cases emerge every year and half of these are sputum smear-positive. Pakistan is also estimated to have the 4th highest prevalence of multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) globally. An observational study in Gulag Devi Chest Hospital, Lahore showed that 44% of patients suffering from P.T.B were elderly. P.T.B was found more in males (60%) as compared to females. All the patients were needy e.g.; most of the patients belonged to poor settings suffering malnutrition. Their financial background was poor. The number of smokers was few(28%). 6% of patients experienced productive cough and 94% of patients experienced more than one symptom which included cough, chest pain, and dyspnea in most of the patients while some experienced body pain and bloody sputum along with cough and fever. All the patients experienced side effects after taking medications for pulmonary tuberculosis. To relieve nausea and vomiting most patients were prescribed To gab inj. Directly observed treatment strategy (DOTs) was seen. DOTs program ensures the right dose, right drug, and right time, that's why all patients were found to be compliant. Lab findings in all patients include sputum smear test. Chest X-ray was done on 100% of patients. Other lab findings were LFT, RFT, Blood tests for ESR, and ENDs for 45% of patients. 100% of patients with suspected pulmonary TB were given the following medicines at first aid: Ampicloxt, FORTA zim, Solucortef, Tigan, and Transamine. To stop bloody sputum Transaminase was used. MYRIN P FORTE Tab was prescribed for all patients with diagnosed P.T.B.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Conclusion
Pakistan ranks 5th globally among the 22 high-burden tuberculosis (TB) countries. Medicines were prescribed by their brand names. DOTs program was observed to ensure patient compliance and prevent resistance to drugs. Lab test for diagnosing P.T.B was sputum for AFB. Chest X-ray was also observed for almost all patients. Other lab findings e.g. LFT, RFT, Blood tests for ESR and WBCs, and test for enzyme Alkaline phosphatase were seen. 1st line and 2nd line medicines were prescribed according to medicines provided by WHO. Side effects such as nausea, body pain, and constipation were observed in patients.
Recommendations
o People working in overcrowded and ill-ventilated places, where the chances of spreading TB are more should be educated about preventive parameters like using masks and gloves.
o Malnutrition increases morbidity due to TB as well as its mortality, especially in resource-poor settings. Poor nutrition affects the immune system and thus predisposes a person to TB. So people must be aware of it.
o 60% of patients were not using masks, as the nose and throat (by inhalation) are the most common points of entry. Mouth (by ingestion) is another point of entry for Mycobacterium Tuberculosis, so patients should be guided.
o Poor air ventilation was seen in hospitals which can predispose healthier to TB. There must be a good ventilation system.
o Pharmacists should come forward to play their role in controlling this highly and speedily prevailing disease.
o They must provide counseling on various aspects of treatment such as dosage instructions, the importance of treatment completion, side effects of drugs, and nutrition during TB.
o Pharmacists should take the lead in collaborating with Government TB authorities to organize patient awareness programs. This could make a significant. Contribution to achieving the millennium development goals for TB control.
Annexure No. 1
Treatment Guidelines by the
National TB Control Program in Pakistan
Table 1
The six essential anti-TB drugs used in the Program,
with their mode of action and dosage (in mg per Kg body weight):
|
Essential
anti-TB drugs (Abbreviation) |
Mode of
action |
Dosage
(mg/kg) |
Common drug
preparations |
|
Isoniazid (H) |
Bactericidal |
5 (4-6) |
Tab: 100mg |
|
Rifampicin
(R) |
Bactericidal |
10 (8-12) |
Tab: 150, 300,450mg |
|
Pyrazinamide (Z) |
Bactericidal |
25 (20-30) |
Tab: 500mg |
|
Streptomycin
(S) |
Bactericidal |
15 (12-18) |
Amp: 1000mg |
|
Ethambutol
(E) |
Bacteriostatic |
15 (12-20) |
Tab: 400mg |
Table
2
Categories of TB Patients
|
Smear Results |
Disease
Classification |
Patient Type |
Category |
|
Positive |
Pulmonary |
New Retreatment: §
Relapse §
Rx.after
failure §
Rx.after
defaults §
Others (s+ only) |
CAT-I
CAT-II |
|
Negative |
Pulmonary or Extra-pulmonary |
New & others(S-only) |
CAT-I |
Table
3
|
Treatment
category |
Initial
intensive phase |
Continuation
phase daily |
|
Category 1 |
FDC containing Rifampicin 150mg, Isoniazid 75mg,
Pyrazinamide 400mg, Ethambutol 275mg (RHZE) for 2 months according to body
weight bands |
FDC containing Rifampicin 150 mg Isoniazid 75mg (RH)
for 4 months according to body weight bands |
|
Category 2 |
FDC containing Rifampicin 150mg, Isoniazid 75mg,
Pyrazinamide 400mg, Ethambutol 275mg, and IInjStreptomycin (500-750 mg)
(RRHZES for 2 months AND Rifampicin, IIsoniazid PPyrazinamide
EEthambutol(RRHZE for 1month according to body weight bands |
FDC containing Rifampicin 150mg, Isoniazid
Ethambutol(RHE) for 4 months according to body weight bands |
Table
4
For Category 1
|
Intensive
phase |
Continuation
phase |
|
Duration in
months: 2 |
Duration in months: 4 |
|
Drugs: HRZE |
RH |
Table
5
For Category 2
|
Intensive
phase |
Continuation
phase |
|
Duration in
months: 3 |
Duration in months: 5 |
|
Drugs: HRZE
plus S |
RHE |
Annexure No. 2
WHO TB control guidelines
Table 6
Recommended doses of first-line antituberculosis drugs
for adults
|
Dose |
|
Recommended
doses |
|
|
|
|
Daily |
|
3 times per
week |
|
|
|
Dose and range (mg/kg body weight) |
Maximum (mg) |
Dose and range (mg/kg body weight) |
Daily maximum (mg) |
|
Isoniazid |
5(4-6) |
300 |
10(8-12) |
900 |
|
Rifampicin |
10(8-12) |
600 |
10(8-12) |
600 |
|
Pyrazinamide |
25(20-30) |
- |
35(30-40) |
- |
|
Ethambutol |
15(15-20) |
- |
30(25-35) |
- |
|
Streptomycin |
15(12-18) |
|
15(12-18) |
1000 |
Patients aged
over 60 years may not be able to tolerate more than 500-750mg daily, so some
guidelines recommend a reduction of the dose to 10mg/kg per day in patients in
this age group.
Patients weighing less than 50kg may not tolerate
doses above 500-750mg daily.
Table 7
Standard regimes for new TB patients(presumed, or
known, to have drug-susceptible TB)
|
Intensive
phase treatment |
Continuation
phase |
|
2 months of
HRZE |
4 months of HR |
Table 8
Standard regimes where isoniazid resistance is high
among new TB cases
|
Intensive
phase treatment |
Continuation
phase |
|
2 months of
HRZE |
4 months of HRE |
Table
9
Dosing frequency for new TB
patients
|
Dosing
frequency |
|
Comment |
|
Intensive
phase |
Continuous
phase |
|
|
Daily |
Daily |
Optimal |
|
Daily |
3 times per week |
Acceptable alternative for any new TB patients
receiving directly observed therapy |
|
3 times per
week |
3 times per week |
An acceptable alternative provided that the patient
receiving directly observed therapy and is not living with HIV or living in
an HIV-prevalent setting |
Table
10
Groups of drugs to treat
MDR-TB
|
Group |
Drugs(abbreviation) |
|
Group 1: First-line
oral agents |
Pyrazinamide(Z) Ethambutol(E) Rifabutin(Rfb) |
|
Group 2: Injectable
agents |
Kanamycin(Km) Amikacin(Am) Capreomycin(Cm) Streptomycin(S) |
|
Group 3: Fluoroquinolones |
Levofloxacin (Lfx) Moxifloxacin(Mfx) Ofloxacin(Ofx) |
|
Group 4 Oral
bacteriostatic second-line agents |
Para-aminosalicylic
acid(PASA) Cycloserine(Cs) Terizidone(Trd) Ethionamide(Eto) Protionamide(Pto) |
|
Group 5 Agents with
unclear roles in the treatment of drug-resistant TB |
Clofazimine(Cfz) Linezolid(Lzd) Amoxicillin/clavulanate(Amx/Clv) Thioacetazone(Thx) Imipenem/cilastin(Imp/Cln) High-dose
isoniazid(high-risk H) Clarithromycin(Clr) |
Group 1
Group 1 drugs are the most potent and best tolerated. If there is good laboratory evidence and clinical history that a drug from this group is effective, it should be used. If group 1 was used in a previous regimen that failed, its efficacy should be rifabutin, have very high rates of cross-resistance to rifampicin.
Group 2
All patients should receive group 2 injectable agents if susceptibility is documented or suspected. Among aminoglycosides, kanamycin or animation is the first choice of an injectable agent, given the high rates of streptomycin resistance in drug-resistant TB. In addition, both these agents are inexpensive, cause less ototoxicity than streptomycin, and have been used extensively for the treatment of drug-resistant TB. Amikacin and kanamycin are considered to be very similar and have a high frequency of cross-resistance. If an isolate is resistant to both serotonin and kanamycin or if DRS data show high rates of resistance to amikacin and kanamycin, vancomycin should be used.
Group 3
All patients should receive a group 3 medication if the M. tuberculosis strain is susceptible or if the agents are thought to have efficacy. One of the higher-generation fluoroquinolones, such as levofloxacin or moxifloxacin, is the fluoroquinolone of choice. Ciprofloxacin is no longer recommended to treat drug-susceptible or drug-resistant TB.
Group 4
Ethionamide is often added to the treatment regimen because of its low cost. If cost is not a constraint, p-aminosalicylic acid may be added first, given that the enteric-coated formulas are relatively well tolerated and that there is no cross-resistance to other agents. When two agents are needed, cycloserine can be added. Since the combination of ethionamide and PAS often causes a high incidence of gastrointestinal side effects and hypothyroidism, these agents are usually used together only when three Group 4 agents are needed: ethionamide, cycloserine, and PAS. Terizidone can be used instead of cycloserine and is assumed to be equally efficacious.
Group 5
Group 5 drugs are not recommended by WHO for routine use in drug-resistant TB treatment because their contributions to the efficacy of multidrug regimens are unclear. They can be used in cases where it is impossible to design adequate regimens with the medicines from Groups 1-4, such as in patients with XDR-TB. They should be used in consultation with an expert in the treatment of drug-resistant TB.
Annexure No. 3
Table
11
Medicines prescribed before
diagnosis (first aid)
|
Sr. No. |
Brand Name |
Generic Name |
Price/cost(Rs.) |
Dose |
Frequency |
|
1 |
Ampiclox tab |
Ampicillin and cloxacillin |
150 |
500mg |
q.i.d |
|
2 |
Carbex plus syrup |
Promethazine and carbocistein |
45 |
2.5mg/ml 100mg/ml |
2 tbs b.i.d |
|
3 |
Mofox tab |
|
200 |
400mg |
o.d |
|
4 |
Trasamine |
Tranexamic acid |
100 |
500mg |
b.i.d |
|
5 |
O2-inhalation |
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
Cefoxin |
Cefoxitin |
|
1g |
b.i.d |
|
7 |
Solucortef |
Hydrocortisone |
86 |
100mg |
b.i.d |
|
8 |
Tagamet |
Cemetidine
|
|
150mg/ml |
t.i.d |
|
9 |
Ventolin nebulizer |
Salbutamol |
200 |
5mg |
t.i.d |
|
10 |
Piritone tab |
Ethenzamide |
150 |
4mg |
q.i.d |
|
11 |
Dexa inj. |
Dexamethasone |
150 |
10mg/ml |
o.d |
|
12 |
Fortazim |
Ceftazidime |
100 |
1g |
b.i.d |
|
13 |
Nopa cap |
Tramadol |
85 |
50mg |
o.d |
Table
12
Medicines prescribed after
diagnosis of Pulmonary TB
|
1 |
Myrin P Fort. |
Rifampicin Isoniazid,
Pyrazinamide |
876.0 |
100mg |
b.i.d |
|
2 |
Panadol |
Mefenmic acid |
30 |
250mg |
b.i.d |
|
3 |
Muconyl syrup |
Guaifenesin, Terbutaline |
27 |
12mg/ml, 0.3mg/ml, 1tbs |
b.i.d |
References
-
Walker, R., & Whittlesea, C. (2007c). Clinical pharmacy and Therapeutics.
Programme, G. T. (2011, January 1). Global tuberculosis control: WHO report 2011. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241564380
- American Lung Association. Tuberculosis. Symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. www.lung.org/lung-disease/tuberculosis/symptoms-diagnosis.html. Accessed February 9, 2012.
- Tavitian, S. M., Spalek, V. H., & Bailey, R. P. (2003). A pharmacist-managed clinic for treatment of latent tuberculosis infection in health care workers. American Journal of Health-system Pharmacy, 60(18), 1856–1861. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajhp/60.18.1856
-
Troy, D. B., & Beringer, P. (2006). Remington: The Science and Practice of Pharmacy. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.Dye, C. (2006). Global epidemiology of tuberculosis. The Lancet, 367(9514), 938-940.
- Programme, G. T. (2011b, January 1). Global tuberculosis control: WHO report 2011. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241564380
-
Tuberculosis in Pakistan: Are we losing the battle? By Abdul Basitwww.jpma.org.pk/full_article_text.php?article_id=234
- Fitzgerald, D., Sterling, T., & Haas, D. (2015). 251 – Mycobacterium tuberculosis. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/251-%E2%80%93-Mycobacterium-tuberculosis-Fitzgerald-Sterling/e3be283e00e375dd678decdcacf7248f6f8af52e
- GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R. Principles and practice of infectious diseases. 7th ed. Philapedia, PA: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2010: 3129-3164
- GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R. Principles and practice of infectious diseases. 7th ed. Philapedia, PA: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2010: 3129-3164
- Corbett EL, Marston B, Churchyard CJ, CDC. Tuberculosis. Basic TB facts. Risk of transmission www.cdc.gov/tb/topic/basics/risk.htm. Accessed March 9, 2012.
- Mazurek, G. H., Jereb, J. A., Vernon, A., Lobue, P. A., Goldberg, S., & Castro, K. G. (2010). Updated guidelines for using Interferon Gamma Release Assays to detect Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection - United States, 2010. PubMed, 59(RR-5), 1–25. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20577159
- Ena, J., & Valls, V. (2005). Short-Course Therapy with Rifampin plus Isoniazid, Compared with Standard Therapy with Isoniazid, for Latent Tuberculosis Infection: A Meta-analysis. Clinical Infectious Diseases/Clinical Infectious Diseases (Online. University of Chicago. Press), 40(5), 670–676. https://doi.org/10.1086/427802
- Jereb, J. A., Goldberg, S., Powell, K. M., Villarino, M. E., & LoBue, P. (2011). Recommendations for use of an isoniazid-rifapentine regimen with direct observation to treat latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Recommendations for Use of an Isoniazid-Rifapentine Regimen With Direct Observation to Treat Latent Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Infection. https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/20846
- Horne, R., Barber, N., Weinman, J., Ra, E., Morgan, M., & Cribb, A. (2006). NHS service delivery and organisation R&D programme: concordance, adherence and compliance in medicine taking. Concordance, Adherence and Compliance in Medicine Taking. https://www.research.manchester.ac.uk/portal/en/publications/nhs-service-delivery-and-organisation-rd-programme-concordance-adherence-and-compliance-in-medicine-taking(5ed745f3-a769-47bd-a54b-09f1c8768e8a)/export.html
- Cramer, J. A., Roy, A., Burrell, A., Fairchild, C., Fuldeore, M., Ollendorf, D. A., & Wong, P. (2008). Medication Compliance and Persistence: Terminology and Definitions. Value in Health, 11(1), 44–47. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4733.2007.00213.x
- Cuneo, W. D., & Snider, D. E. (1989). Enhancing Patient Compliance with Tuberculosis Therapy. Clinics in Chest Medicine, 10(3), 375–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0272-5231(21)00640-7
- WHO (2006). An expanded DOTS framework for effective tuberculosis control. (2002). PubMed, 6(5), 378–388. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12019913
- Last, J. M., & Kozakiewicz, J. (2009). Development of a pharmacist-managed latent tuberculosis clinic. American Journal of Health-system Pharmacy, 66(17), 1522–1523. https://doi.org/10.2146/ajhp090034
- Clark, P. M., Karagöz, T., Apikoğlu-Rabuş, Ş., & İzzettin, F. (2007). Effect of pharmacist-led patient education on adherence to tuberculosis treatment. American Journal of Health-system Pharmacy, 64(5), 497–505. https://doi.org/10.2146/ajhp050543
-
(MMWR, 2003). Update: Adverse event data and Revised American Thoracic Society/CDC recommendations against the use of rifampin and pyrazinamide for treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection---United States, 2003. (2003, August 8). https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm5231a4.htm
-
Walker, R., & Whittlesea, C. (2007c). Clinical pharmacy and Therapeutics.
Programme, G. T. (2011, January 1). Global tuberculosis control: WHO report 2011. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241564380
- American Lung Association. Tuberculosis. Symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. www.lung.org/lung-disease/tuberculosis/symptoms-diagnosis.html. Accessed February 9, 2012.
- Tavitian, S. M., Spalek, V. H., & Bailey, R. P. (2003). A pharmacist-managed clinic for treatment of latent tuberculosis infection in health care workers. American Journal of Health-system Pharmacy, 60(18), 1856–1861. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajhp/60.18.1856
-
Troy, D. B., & Beringer, P. (2006). Remington: The Science and Practice of Pharmacy. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.Dye, C. (2006). Global epidemiology of tuberculosis. The Lancet, 367(9514), 938-940.
- Programme, G. T. (2011b, January 1). Global tuberculosis control: WHO report 2011. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241564380
-
Tuberculosis in Pakistan: Are we losing the battle? By Abdul Basitwww.jpma.org.pk/full_article_text.php?article_id=234
- Fitzgerald, D., Sterling, T., & Haas, D. (2015). 251 – Mycobacterium tuberculosis. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/251-%E2%80%93-Mycobacterium-tuberculosis-Fitzgerald-Sterling/e3be283e00e375dd678decdcacf7248f6f8af52e
- GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R. Principles and practice of infectious diseases. 7th ed. Philapedia, PA: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2010: 3129-3164
- GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R. Principles and practice of infectious diseases. 7th ed. Philapedia, PA: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2010: 3129-3164
- Corbett EL, Marston B, Churchyard CJ, CDC. Tuberculosis. Basic TB facts. Risk of transmission www.cdc.gov/tb/topic/basics/risk.htm. Accessed March 9, 2012.
- Mazurek, G. H., Jereb, J. A., Vernon, A., Lobue, P. A., Goldberg, S., & Castro, K. G. (2010). Updated guidelines for using Interferon Gamma Release Assays to detect Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection - United States, 2010. PubMed, 59(RR-5), 1–25. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20577159
- Ena, J., & Valls, V. (2005). Short-Course Therapy with Rifampin plus Isoniazid, Compared with Standard Therapy with Isoniazid, for Latent Tuberculosis Infection: A Meta-analysis. Clinical Infectious Diseases/Clinical Infectious Diseases (Online. University of Chicago. Press), 40(5), 670–676. https://doi.org/10.1086/427802
- Jereb, J. A., Goldberg, S., Powell, K. M., Villarino, M. E., & LoBue, P. (2011). Recommendations for use of an isoniazid-rifapentine regimen with direct observation to treat latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Recommendations for Use of an Isoniazid-Rifapentine Regimen With Direct Observation to Treat Latent Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Infection. https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/20846
- Horne, R., Barber, N., Weinman, J., Ra, E., Morgan, M., & Cribb, A. (2006). NHS service delivery and organisation R&D programme: concordance, adherence and compliance in medicine taking. Concordance, Adherence and Compliance in Medicine Taking. https://www.research.manchester.ac.uk/portal/en/publications/nhs-service-delivery-and-organisation-rd-programme-concordance-adherence-and-compliance-in-medicine-taking(5ed745f3-a769-47bd-a54b-09f1c8768e8a)/export.html
- Cramer, J. A., Roy, A., Burrell, A., Fairchild, C., Fuldeore, M., Ollendorf, D. A., & Wong, P. (2008). Medication Compliance and Persistence: Terminology and Definitions. Value in Health, 11(1), 44–47. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4733.2007.00213.x
- Cuneo, W. D., & Snider, D. E. (1989). Enhancing Patient Compliance with Tuberculosis Therapy. Clinics in Chest Medicine, 10(3), 375–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0272-5231(21)00640-7
- WHO (2006). An expanded DOTS framework for effective tuberculosis control. (2002). PubMed, 6(5), 378–388. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12019913
- Last, J. M., & Kozakiewicz, J. (2009). Development of a pharmacist-managed latent tuberculosis clinic. American Journal of Health-system Pharmacy, 66(17), 1522–1523. https://doi.org/10.2146/ajhp090034
- Clark, P. M., Karagöz, T., Apikoğlu-Rabuş, Ş., & İzzettin, F. (2007). Effect of pharmacist-led patient education on adherence to tuberculosis treatment. American Journal of Health-system Pharmacy, 64(5), 497–505. https://doi.org/10.2146/ajhp050543
-
(MMWR, 2003). Update: Adverse event data and Revised American Thoracic Society/CDC recommendations against the use of rifampin and pyrazinamide for treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection---United States, 2003. (2003, August 8). https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm5231a4.htm
Cite this article
-
APA : Arshad, A., Abaidullah, R., & Bakhtiari, M. N. (2023). An Observational Study for the Management of Tuberculosis at the Public Hospital of Lahore, Pakistan. Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VIII(III), 1-17. https://doi.org/10.31703/gpsr.2023(VIII-III).01
-
CHICAGO : Arshad, Anam, Rimsha Abaidullah, and Maria Naz Bakhtiari. 2023. "An Observational Study for the Management of Tuberculosis at the Public Hospital of Lahore, Pakistan." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VIII (III): 1-17 doi: 10.31703/gpsr.2023(VIII-III).01
-
HARVARD : ARSHAD, A., ABAIDULLAH, R. & BAKHTIARI, M. N. 2023. An Observational Study for the Management of Tuberculosis at the Public Hospital of Lahore, Pakistan. Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VIII, 1-17.
-
MHRA : Arshad, Anam, Rimsha Abaidullah, and Maria Naz Bakhtiari. 2023. "An Observational Study for the Management of Tuberculosis at the Public Hospital of Lahore, Pakistan." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VIII: 1-17
-
MLA : Arshad, Anam, Rimsha Abaidullah, and Maria Naz Bakhtiari. "An Observational Study for the Management of Tuberculosis at the Public Hospital of Lahore, Pakistan." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VIII.III (2023): 1-17 Print.
-
OXFORD : Arshad, Anam, Abaidullah, Rimsha, and Bakhtiari, Maria Naz (2023), "An Observational Study for the Management of Tuberculosis at the Public Hospital of Lahore, Pakistan", Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VIII (III), 1-17
-
TURABIAN : Arshad, Anam, Rimsha Abaidullah, and Maria Naz Bakhtiari. "An Observational Study for the Management of Tuberculosis at the Public Hospital of Lahore, Pakistan." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review VIII, no. III (2023): 1-17. https://doi.org/10.31703/gpsr.2023(VIII-III).01
