Abstrict
To assess the quality of life of Covid- 19 survivors with co-morbidities, association with gender and impact on their physical, and mental health, pain, self-care, and social activities. An online descriptive study was carried out in Khyber Pukhtoon Khwa from 12th January- 2021 to 12th March- 2021, with a 377 sample size from Raosoft online calculator. All COVID-19-recovered individuals with co-morbidities, a negative PCR, aged 18 and above, literate, residents of Peshawar and having smartphone/laptop/ internet access were included while the ones having no consent, hospitalized and severe patients were excluded from the study. Descriptive statistics with frequency, percentage, mean and standard deviation however, inferential statistics were calculated for associations through Chi-square and paired t-tests with a significant p-value set at 0.05. The survey response rate was 51.4 % (n=193) out of 377. The participants had a mean age of 35 years (SD= 10.207, range= 16- 70 years). The highest responses were received from 22 years of age (26.3 %). The EQ5D mean score was 1.227 (SD= 1.89). The most frequently reported problem was anxiety/depression (54.8%) followed by pain/discomfort (46.8%), problems with usual activities (39.6%), mobility (26.7%) and self-care (15.1%). EQ5D showed a strong association with chronic diseases and significant p values for mobility, usual activities, and pain/discomfort (0.000) with 0.003 for anxiety/depression. COVID-19 survivors were associated with a substantial measurable decrease in their quality of life.
Keywords
COVID-19, Persistent Symptoms, Health-Related Quality of Life, Health Disparities, Disabilities, Mental Health
Introduction
Viral diseases continue to emerge and present a significant threat to public health. The coronavirus is an infectious disease in humans. The first case was reported in Wuhan-China in late December 2019. (WHO 2020) Soon after its emergence it became an outbreak and by mid-March 2020. WHO declared it as a global pandemic due to the rapid spread of this disease thereby affecting countries worldwide. (Cucinotta 2020) Covid-19 spread frequency was estimated to be at 4.08, and each individual case was responsible to add up four more cases further. Since its start, the cases reported so far have alarmingly increased by 21-fold and WHO claims the fatality rate of covid-19 to be 2%. WHO and the health care authorities worldwide took an active part in the control of its spread, as this crisis had a very significant effect on human health and wellbeing causing psychological distress, anxiety and panic in the masses. (Wang 2020) Covid- 19 in Pakistan became worse with time and reported 420, 000 people and more than 8, 300 attributed deaths. Pakistan faced the consequences of this pandemic with the poverty level at 33.7% further causing economic loss, changes in environmental factors and social effects. (Rasheed 2021).
A Chinese Survey of the elderly population depicted them as the most vulnerable population to Covid-19 with weak immune systems with high levels of psychological stress. Japanese individuals showed dismissal, accusation and segregation from society, which in turn deteriorated their physical health and lowered life expectancy. Every country during the pandemic situation tried to tackle the problem with their own resources and carried out research too for baseline data. A Moroccan study was carried out after two months of the quarantine period for Covid-19. Quality of life was measured and found to not only affected the diseased persons but healthy individuals as well. Many foreign types of research have been conducted on quality of life (QoL) among Covid-19 survivors. A Chinese online survey used the Euro Quality of Life 5- Dimension (EQ-5D) scale with five health dimensions and provided health-related quality of life during the pandemic situation. Another online health-related QoL survey also used EQ- 5D research tool. An Indian study was conducted through online applications and COVID-19 anxiety was measured through a six-item scale of five from never (0) to always (4). Higher scores indicated high anxiety and likewise. (Kharshiing 2020)
A Pakistani Online Survey used SF-12 (Short Form Health Survey) and analyzed post-Covid QoL and symptoms among 331 persons from all over Pakistan, and noted variables such as fever, diarrhoea, headache, body aches, loss of smell, low mood and cough. After the early Covid- 19 pandemic another Online Pakistani study was conducted in Punjab with 1002 adult participants of 19- 45 years of age, to determine the direct and indirect relationship between obsession, stress, satisfaction and purpose in life. A descriptive study conducted in Hyderabad in six months from 2021- 2022 used the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS) and quality of life assessed through 16 items scale of 158 individuals.
Quality of life assessment in post covid recovered patients and especially with comorbidities has been a neglected subject and very scarce data is available in this province. Such a study has not been done in Pakistan to the best of the researcher's knowledge and internet browsing. To get information and baseline data, this present study was planned to assess the quality of life among the Covid- 19 survivors with comorbidities, determine an association with gender, and the impact on their physical, and mental health, pain, self-care and social activities.
Methodology
A descriptive study was conducted as an online survey in Peshawar- Khyber Pukhtoon Khwa in two months duration from 12th January- 2021 to 12th March- 2021. The sample size of 377 was calculated from an online calculator, with a 5% margin of error, 50 % distribution rate and 95% confidence interval. Among the total only 194 participants completed it, and one went missing with a response rate of 51.4 %. Ethical approval was taken from Institutional Ethical Review Board Committee (IERC) (ERC Approval Number: Prime/ERC/2020- 05).
Euro Quality of Life 5-dimension (EQ- 5D) was used to assess the quality of life with mobility, self-care, usual activities, pain/discomfort, and anxiety/depression. The scores for this scale range from 0 meant for death and 1 for perfect health. The EQ-5D questionnaire had a Visual Analog Scale (VAS), ranging from 0 (the worst possible health status) to 100 (the best possible health status) for the overall health status. Another also tool used was HRQOL, which was for adults, designed for clinical use, short and easy to administer for social, physical and psychosocial domains with easy scoring criteria.
All COVID-19-recovered individuals with negative PCR, aged 18 and above, literate, having smartphone/laptop/ internet access and KPK residents with an agreement to participate were recruited through a purposive sampling technique. Whereas, all Post COVID- 19 recovered individuals with negative PCR who refused or did not consent to participate; hospitalized, post-COVID-19
Serious persons, admitted in ICUs (Intensive Care Units) and
CCUs (Cardiac Care Units) were excluded from the study.
The variables assessed were age, sex, educational status, occupation, monthly income, location, marital status, any chronic disease, any fear of Covid- 19, when covid test is done, covid influence on social activities, marital life, diet patterns, sleep, working stability, exercise, relations with parents, learning, income, relations with friends and on children education. More variables assessed in terms of health status were mobility, self-care, activities, pain/discomfort and depression/ anxiety. Ethical considerations were duly taken care of with the voluntary induction of the participants. Informed consent and confidentiality were maintained at all levels regarding consent, data storage and management. The 4th Year MBBS students collected the data through the Whatsapp link online. The data was entered and analyzed in SPSS Version- 21 through descriptive statistics such as frequency, percentages, mean and standard deviation. Whereas, inferential statistics for association and comparison were done through chi-square and t-test application keeping 0.05 as the significant limit.
Results
The questionnaire of this study was distributed online, all over KPK. Out of the total 194 responses, 99.4% (n= 193) were valid whereas 1% (n= 1) were missing with a response rate of 51.19 %. The participants had a mean age of 35 years (SD= 10.207, range= 16- 70 years). The highest number of responses were received from 22 years' age persons with 26.3 %.
As per gender analysis, 65.28 % (n= 126) were females, 34.71 % (n= 67) were men and all from KPK. The male-to-female ratio was almost 1:2 with 34.71 % males and 65. 28 % females. Among the total respondents, 25.9 % (n= 50) were married, 0.5 % (n= 1) were divorced and 74.09 % (n= 143) were single/ unmarried.
University-level education was completed by 183 respondents (94.5 %), primary education by only 1 (0.51 %), secondary education by (n= 7; 3.6 %) and matriculates were (n= 3; 1.6 %). Full-time employed came out to be 36.9% (n= 65), retired individuals were 1.7 % (n= 3), people residing at home were 27.3 % (n= 48) and jobless were 34.1 % (n= 60).
The chronic disease sufferers among the 188 respondents were 21.3% (n= 40.04) only. Among the 53 chronic disease respondents, 45.3% (n= 24) were suffering from hypertension, respiratory diseases were seen 22.6% (n= 11.978), 11.3% (n= 5.89) had diabetes, 9.4 (n= 4.98) with kidney problems, 7.5% (n= 3.97) had neurological issues and 3.9% (n= 2) with cardiac problems.
All the respondents were worried about COVID-19 and its recurrence. When asked from 156 participants, 14.1% (n= 21.9) were very much worried about this, 11.55 (n= 17.94) were worried, 29.5% (n= 46) were slightly worried and 44.9% (n= 70) were not worried at all.
In relation to the health dimensions, among the total participants (n=184) 73.4% had no problem in walking around however, 8.2% were confined to bed with 18.5% with some problem in walking and activities performances. Self-care in post covid survivors with co-morbidities was answered by a total of 186 participants, out of which 1.7% were unable to wash themselves and dress up. Some problem was faced by 13.4% however, 84.9% had no problem at all. The usual activities including work, housework and leisure activities were answered by (n=187) people. Such activities were unable to be performed by 5.9%, 33.7% faced some problems and 60.4% had no issue with the performance of these activities. Extreme pain and discomfort were felt by 3.2%, moderate pain and discomfort by 43.6% and 53.2% were without any pain and discomfort. Anxiety and depression were the hallmark of post-covid survivors but 11.2% were extremely depressed, 43.6% had moderate anxiety and depression whereas, 45.2% were devoid of any anxiety and depression.
The association of post-covid persons with chronic diseases in relation to the five health dimensions i. e mobility, self-care, usual activities, pain/ and anxiety/ depression is shown in detail under Table-1.
Table 1
Association of COVID Survivors with Chronic Diseases with Health Dimensions.
|
|
Paired
Differences |
t |
DF |
Sig. (2-tailed) |
|||||
|
Mean |
S. D |
Std. Error Mean |
95% Confidence
Interval of the Difference |
||||||
|
Lower |
Upper |
||||||||
|
Pair 1 |
q8 – mobility |
1.981 |
2.110 |
0.293 |
1.393 |
2.568 |
6.771 |
51 |
0.000 |
|
Pair 2 |
q8 – self-care |
1.327 |
1.779 |
0.247 |
.832 |
1.822 |
5.378 |
51 |
0.000 |
|
Pair 3 |
q8 – usual
activities |
1.038 |
1.815 |
0.252 |
.533 |
1.544 |
4.127 |
51 |
0.000 |
|
Pair 4 |
q8 –
pain/discomfort |
0.942 |
1.809 |
0.251 |
.439 |
1.446 |
3.757 |
51 |
0.000 |
|
Pair 5 |
q8
–anxiety/depression |
0.846 |
1.954 |
0.271 |
.302 |
1.390 |
3.122 |
51 |
0.003 |
Note: S.D- Standard Deviation; DF;
Degree of Freedom; t; t-Test.
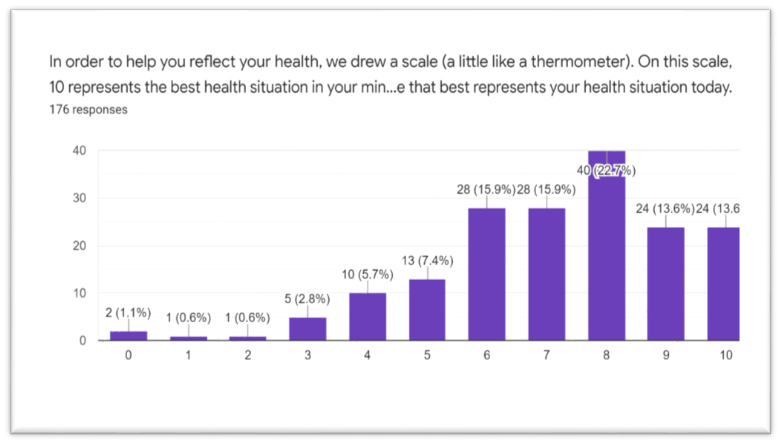
Graph-1 shows a
health scale of the COVID respondents (176/ 193) with their present situation.
Graph 1
Health Scale of the Post-Covid Survivors in their Present Health Status of 176 Participants.
Note: 0 Represents the Worst Health. 10 means Best Health.
Discussion
This study assessed the quality of life among COVID Survivors with co-morbidities in residents of KPK Pakistan. The researchers used the EQ-5D scale for the assessment with its visual component and HRQoL. The findings showed
Covid-19 pandemic with a highly negative impact on the education status of responders at 23.4% followed by social activities at 20.21%, working stability at 19.6%, income at 18.6%, daily life at 13% and least impact on relationships at 7.9%. COVID influence on a variety of parameters like social activities, daily life, sleep, exercise, diet, working stability, relationships with parents and friends, marital bonding and children’s education as well. Negative Covid influences were found on social activities, daily life routines, individuals' diet consumption, sleep patterns of covid survivors, and working stability. However, slightly negative effect on relationships with parents and friends, and marital relationships with a greatly negative effect on children learning and education patterns.
A Moroccan online descriptive study used SF-12 form with eight dimensions to determine the quality of life during the quarantine period of emergency covid-19. The results revealed lower scores in mental and physical health with chronic diseases. Quality of life was compromised and poor among elderly people with chronic diseases during the pandemic. These results correlate with the present study with the same mean age and low quality of life however, the tools used were different. (Samlani 2020) The findings of a Chinese survey showed a significantly higher risk of discomfort and depression among the assessed population with chronic diseases, similar to the present study. Both studies used the same tool, population and objectives. (Ping 2020) A study took data from the 2005 Health Survey, emailed it to the participants, used EQ-5 as a tool and measured the HRQOL of Japanese. The results confirmed decreased scores in relation to EQ-5 among the elderly, retired and unemployed persons. (Fujikawa 2011) These were exactly similar to the present study in methodology, tool and in terms of outcome scores. The association of Covid anxiety, severity and perceived susceptibility was evaluated with quality of life and predicted as significantly correlated with the compromised quality of life in an online study. These outcomes were congruent with the existing study as well, although the assessment tools were entirely different. (Kharshiing 2020).
A Pakistani online survey used SF-12 for quality-of-life assessment and found poor quality of life with low mood and disturbed mental health in post- covid patients same as this study with difference of tool only. (Qamar 2022) Another Pakistani mediation study used stress and obsession evaluation with the satisfaction of life. The purposeful and meaningful life of the person showed low stress/ obsessions and vice versa. (Ashraf 2021) This study was entirely different from the present one in methodology. One more study from Pakistan recruited PCR-negative persons and determined depression among post covid survivors as well as the quality of life through HDRS. Most of them had mild to moderate depression and average life satisfaction among the participants, exactly the same as the present study results but other dimensions of health were overlooked. (Ali 2022) The impact of Covid-19 on psychological well-being with associated factors was evaluated through World Health Organization's Well-Being Index-5 (WHO-5) in an online Pakistani study. The general population was found to be of poor well-being with being jobless, female gender, Sind resident and chronic illness and fear as the risk factors involved. These are in line with the current study findings. (Khan 2021)
An Online study observed the Covid-19 pandemic effects on the population's quality of life via a self-structured questionnaire same as in this study but with variant tools of assessment. Significant stress, low mental health and poor quality of life were revealed among men, housewives and the elderly just like in the present study. (Hanumantha 2021) A Prospective Online survey showed Covid-19's impact on the quality of life of families, by using standardized EQ-5D-3L. The results depicted were similar to the present study with maximum pain/discomfort, usual activities problems, anxiety/depression, and mobility problems. Moreover, those with chronic health conditions showed pronounced changes in all the assessed parameters. Self-care was compromised with sadness, loneliness and being frustrated. (Shah 2021) An Egyptian Community based study determined Post Covid-19 effects through interviews among the adult population. The lowest mean scores were related to mental health deterioration and the highest mean scores were for dangers/fear with quality of life. The predictors for these effects were sex, income, and covid reinfections. Although in terms of QOL, the findings are the same, however, differ in methodology only. (Mohsen 2022).
HRQOL was measured through EQ-5-3L with factors responsible for the Covid infection. These results are exactly similar to the present study and showed deranged HRQOL among the post covid, elderly and the ones with chronic illnesses. Asthma was found to be significantly related to low quality of life. (Kaso 2021)Compromised and poor HRQOL was found in areas of pain/discomfort with daily activities in a Multicenter French study one year after the pandemic. 21. (Tarazona 2022) same areas were also identified with greater frequency in this study as well. An Arabic version of QOL was used in a study to check Covid-19 after effects and found low scores in mental and spiritual health with age as strongly related to these variables, 22. (Algamdi 2021) quite similar to the present study. A Systematic Review found poor quality of life in post covid persons and no associations were found with any variables. However, females, co-morbidities, old age and long stays in hospitals were the identifying factors (Nandasena 2021) exactly like the outcomes of this study. A Saudi study used WHOQOL-BREF to determine the quality of life and associated factors for Covid-19 and found chronic diseases, depression and anxiety to be predictors for the altered changes in their lives. (Algahtani 2021) This study's results were comparable with the present one but the tools used were different.
Limitations: This was an online cross-sectional study so no face-to-face interaction was possible at that time and the link between the outcome and exposure could not be determined because both were examined at the same time. In this study, the most affected age group were not categorized, and also which co-morbidity had a high link with the quality of life in COVID-19 survivors. Another problem with this was total number of participants was 193 but every question was not completed by an equal number.
Conclusion
COVID-19 is associated with a substantial and measurable decrease in HRQoL. This study's results confirmed the need to pay attention to the health of people with chronic illnesses who have been infected with a virus.
References
- Algahtani, F. D., Hassan, S.U., Alsaif, B., & Zrieq, R. (2021). Assessment of the Quality of Life during COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Survey from the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 18(3), 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18030847.
- Algamdi, M. M. (2021). Assessment of Post-COVID- 19 Quality of Life Using the Quality-of-Life Index. Patient Prefer Adherence. 15, 2587- 2596. https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S340868
- Ali, M., Jatoi, S., Maheshwari, S., Bawany, M. A., & Bukhari, D. (2022). Depression among Survivors of Covid-19 Infection and Its Impact on the Quality of Life. APMC. 16(1), 41- 44. https://doi.org/10.29054/apmc/2022.955
- Ashraf, F., Zareen, G., Nusrat, A., Arif, A., & Griffiths, M. D. (2021). Correlates of Psychological Distress among Pakistani Adults during the COVID-19 Outbreak: Parallel and Serial Mediation Analyses. Frontiers in Psychology. 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.647821
- Balestroni, G., & Bertolotti, G. (2012). [EuroQol-5D (EQ-5D): an instrument for measuring the quality of life]. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis . 78 (3), 155– 59. https://doi.org/10.4081/monaldi.2012.121
- Cucinotta, D., & Vanelli, M. (2020). WHO declares COVID-19 a pandemic. Acta bio-medica. 91 (1), 157– 160. https://doi.org/10.23750/abm.v91i1.9397.
- Fujikawa, A., Suzue, T., Jitsunari, F., & Hirao, T. (2011). Evaluation of health-related quality of life using EQ-5D in Takamatsu, Japan. Environ Health Prev Med. 16, 25– 35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12199-010-0162-1
- Hanumantha, K. R., Naik, P., Varma, L., Varma, M., Manipal, S., & Sampath, P. (2021). Assessment of quality of life in patients after COVID-19 infection: A questionnaire-based observational study. Asian Journal of Medical Sciences. 12 (8), 9– 15: https://doi.org/10.3126/ajms.v12i8.37649
- Kaso, A. W., Agero, G., Hurisa, Z., Kaso, T., Ewune, H. A., & Hailu, A. (2021). Evaluation of health- related quality of life of Covid-19 patients: a hospital-based study in South Central
- Kharshiing, K.D., Kashyap, D., Gupta, K., Khursheed, M., Shahnawaz, M. G, Khan, N. H., Uniyal, R., & Rehman, U. (2020). Quality of Life in the COVID-19 Pandemic in India: Exploring the Role of Individual and Group Variables. Community Mental Health Journal. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10597-020-00712-6
- Meng, H., Xu, Y., Dai, J., Zhang, Y., Liu, B., & Yang, H. (2020). Analyze the psychological impact of COVID-19 among the elderly population in China and make corresponding suggestions. Psychiatry Res. 289, 112983: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2020.11298 3.
- Mohsen, S., El-Masry, R., Ali, O. F., & Hady, D. A. (2022). Quality of life during COVID-19 pandemic: a community-based study in Dakahlia governorate, Egypt. Glob Health res policy 7(15). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41256-022-00246-2
- Nandasena, HMRKG., Pathirathna, M. L., Atapattu, AMMP., & Prasanga, P. T. S. (2021). Quality of life of COVID-19 patients after discharge: Systematic review. PLoS ONE. 17(2). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0263941
- Ping, W., Zheng, J., Niu, X., Guo, C., Zhang, J., & Yang, H. (2020). Evaluation of health-related quality of life using EQ-5D in China during the COVID-19 pandemic. PLoS ONE. 15(6). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0234850
- Qamar, M. A., Martins, R. S., Dhillon, R. A., Tharwani, A., Irfan, O., & Suriya, Q. F. (2022). Residual symptoms and the quality of life in individuals recovered from COVID-19 infection: A survey from Pakistan. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 75. 103361: http://doi.org/10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103361.
- Rasheed, R., Rizwan, A., Javed, H., Shareef, F., &Zaidi, A. (2021). Socio-economic and environmental impacts of COVID-19 pandemic in Pakistan—an integrated analysis. Environ Sci Rasheed, R., Rizwan, A., Javed, H., Shareef, F., &Zaidi, A. (2021). Socio-economic and environmental impacts of COVID-19 pandemic in Pakistan—an integrated analysis. Environ Sci
- Samlani, Z., Lemfadli, Y., Errami, A. A, Oubaha, S., & Krati, K. (2020). The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on quality of life and well-being in Morocco. Arch Community Med Public Health. 6(2), 130- 134 . https://dx.doi.org/10.17352/2455-5479.000091
- Shah, R., Ali, F. M., & Nixon, S. J . (2021). Measuring the impact of COVID-19 on the quality of life of the survivors, partners and family members: a cross-sectional international online survey. BMJ Open. 11. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2020-047680
- Shigemura, J., Ursano, R. J., Morganstein, J. C., Kurosawa, M., & Benedek, D. M. (2020). Public responses to the novel 2019 coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in Japan: Mental health consequences and target populations. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 74(4), 281- 282. https://doi.org/10.1111/pcn.12988
- Tarazona, V., Kirouchena, D., Clerc, P., Pinsard- Laventure, F., & Bourrion, B. (2022). Quality of Life in COVID-19 Outpatients: A Long-Term Follow-Up Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 11 (21), 6478. http s://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216478
- Wang, C., Pan, R., Wan, X., Tan, Y., Xu, L., & Ho, C. S. (2020). Immediate psychological responses and associated factors during the initial stage of the 2019 coronavirus disease (COVID-19) epidemic among the general population in China. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 17 (5), 1729 . https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17051729
- WHO. (2020). Pneumonia of unknown cause– China: World Health Organization . https://www.who.int/csr/don/05-january-2020-pneumonia-of-unkown-cause-china/en/ .
- Algahtani, F. D., Hassan, S.U., Alsaif, B., & Zrieq, R. (2021). Assessment of the Quality of Life during COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Survey from the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 18(3), 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18030847.
- Algamdi, M. M. (2021). Assessment of Post-COVID- 19 Quality of Life Using the Quality-of-Life Index. Patient Prefer Adherence. 15, 2587- 2596. https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S340868
- Ali, M., Jatoi, S., Maheshwari, S., Bawany, M. A., & Bukhari, D. (2022). Depression among Survivors of Covid-19 Infection and Its Impact on the Quality of Life. APMC. 16(1), 41- 44. https://doi.org/10.29054/apmc/2022.955
- Ashraf, F., Zareen, G., Nusrat, A., Arif, A., & Griffiths, M. D. (2021). Correlates of Psychological Distress among Pakistani Adults during the COVID-19 Outbreak: Parallel and Serial Mediation Analyses. Frontiers in Psychology. 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.647821
- Balestroni, G., & Bertolotti, G. (2012). [EuroQol-5D (EQ-5D): an instrument for measuring the quality of life]. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis . 78 (3), 155– 59. https://doi.org/10.4081/monaldi.2012.121
- Cucinotta, D., & Vanelli, M. (2020). WHO declares COVID-19 a pandemic. Acta bio-medica. 91 (1), 157– 160. https://doi.org/10.23750/abm.v91i1.9397.
- Fujikawa, A., Suzue, T., Jitsunari, F., & Hirao, T. (2011). Evaluation of health-related quality of life using EQ-5D in Takamatsu, Japan. Environ Health Prev Med. 16, 25– 35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12199-010-0162-1
- Hanumantha, K. R., Naik, P., Varma, L., Varma, M., Manipal, S., & Sampath, P. (2021). Assessment of quality of life in patients after COVID-19 infection: A questionnaire-based observational study. Asian Journal of Medical Sciences. 12 (8), 9– 15: https://doi.org/10.3126/ajms.v12i8.37649
- Kaso, A. W., Agero, G., Hurisa, Z., Kaso, T., Ewune, H. A., & Hailu, A. (2021). Evaluation of health- related quality of life of Covid-19 patients: a hospital-based study in South Central
- Kharshiing, K.D., Kashyap, D., Gupta, K., Khursheed, M., Shahnawaz, M. G, Khan, N. H., Uniyal, R., & Rehman, U. (2020). Quality of Life in the COVID-19 Pandemic in India: Exploring the Role of Individual and Group Variables. Community Mental Health Journal. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10597-020-00712-6
- Meng, H., Xu, Y., Dai, J., Zhang, Y., Liu, B., & Yang, H. (2020). Analyze the psychological impact of COVID-19 among the elderly population in China and make corresponding suggestions. Psychiatry Res. 289, 112983: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2020.11298 3.
- Mohsen, S., El-Masry, R., Ali, O. F., & Hady, D. A. (2022). Quality of life during COVID-19 pandemic: a community-based study in Dakahlia governorate, Egypt. Glob Health res policy 7(15). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41256-022-00246-2
- Nandasena, HMRKG., Pathirathna, M. L., Atapattu, AMMP., & Prasanga, P. T. S. (2021). Quality of life of COVID-19 patients after discharge: Systematic review. PLoS ONE. 17(2). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0263941
- Ping, W., Zheng, J., Niu, X., Guo, C., Zhang, J., & Yang, H. (2020). Evaluation of health-related quality of life using EQ-5D in China during the COVID-19 pandemic. PLoS ONE. 15(6). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0234850
- Qamar, M. A., Martins, R. S., Dhillon, R. A., Tharwani, A., Irfan, O., & Suriya, Q. F. (2022). Residual symptoms and the quality of life in individuals recovered from COVID-19 infection: A survey from Pakistan. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 75. 103361: http://doi.org/10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103361.
- Rasheed, R., Rizwan, A., Javed, H., Shareef, F., &Zaidi, A. (2021). Socio-economic and environmental impacts of COVID-19 pandemic in Pakistan—an integrated analysis. Environ Sci Rasheed, R., Rizwan, A., Javed, H., Shareef, F., &Zaidi, A. (2021). Socio-economic and environmental impacts of COVID-19 pandemic in Pakistan—an integrated analysis. Environ Sci
- Samlani, Z., Lemfadli, Y., Errami, A. A, Oubaha, S., & Krati, K. (2020). The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on quality of life and well-being in Morocco. Arch Community Med Public Health. 6(2), 130- 134 . https://dx.doi.org/10.17352/2455-5479.000091
- Shah, R., Ali, F. M., & Nixon, S. J . (2021). Measuring the impact of COVID-19 on the quality of life of the survivors, partners and family members: a cross-sectional international online survey. BMJ Open. 11. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2020-047680
- Shigemura, J., Ursano, R. J., Morganstein, J. C., Kurosawa, M., & Benedek, D. M. (2020). Public responses to the novel 2019 coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in Japan: Mental health consequences and target populations. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 74(4), 281- 282. https://doi.org/10.1111/pcn.12988
- Tarazona, V., Kirouchena, D., Clerc, P., Pinsard- Laventure, F., & Bourrion, B. (2022). Quality of Life in COVID-19 Outpatients: A Long-Term Follow-Up Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 11 (21), 6478. http s://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216478
- Wang, C., Pan, R., Wan, X., Tan, Y., Xu, L., & Ho, C. S. (2020). Immediate psychological responses and associated factors during the initial stage of the 2019 coronavirus disease (COVID-19) epidemic among the general population in China. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 17 (5), 1729 . https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17051729
- WHO. (2020). Pneumonia of unknown cause– China: World Health Organization . https://www.who.int/csr/don/05-january-2020-pneumonia-of-unkown-cause-china/en/ .
Cite this article
-
APA : Malik, F. R., Iqbal, H. J., & Sumbal, H. (2023). An Evaluation of Quality-of-Life Assessment among Post Covid- 19 Survivors with Co-Morbidities & Impact Upon their Physical and Mental Health. Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VIII(I), 16-23. https://doi.org/10.31703/gpsr.2023(VIII-I).03
-
CHICAGO : Malik, Farhat R., Hira Javed Iqbal, and Hira Sumbal. 2023. "An Evaluation of Quality-of-Life Assessment among Post Covid- 19 Survivors with Co-Morbidities & Impact Upon their Physical and Mental Health." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VIII (I): 16-23 doi: 10.31703/gpsr.2023(VIII-I).03
-
HARVARD : MALIK, F. R., IQBAL, H. J. & SUMBAL, H. 2023. An Evaluation of Quality-of-Life Assessment among Post Covid- 19 Survivors with Co-Morbidities & Impact Upon their Physical and Mental Health. Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VIII, 16-23.
-
MHRA : Malik, Farhat R., Hira Javed Iqbal, and Hira Sumbal. 2023. "An Evaluation of Quality-of-Life Assessment among Post Covid- 19 Survivors with Co-Morbidities & Impact Upon their Physical and Mental Health." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VIII: 16-23
-
MLA : Malik, Farhat R., Hira Javed Iqbal, and Hira Sumbal. "An Evaluation of Quality-of-Life Assessment among Post Covid- 19 Survivors with Co-Morbidities & Impact Upon their Physical and Mental Health." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VIII.I (2023): 16-23 Print.
-
OXFORD : Malik, Farhat R., Iqbal, Hira Javed, and Sumbal, Hira (2023), "An Evaluation of Quality-of-Life Assessment among Post Covid- 19 Survivors with Co-Morbidities & Impact Upon their Physical and Mental Health", Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review, VIII (I), 16-23
-
TURABIAN : Malik, Farhat R., Hira Javed Iqbal, and Hira Sumbal. "An Evaluation of Quality-of-Life Assessment among Post Covid- 19 Survivors with Co-Morbidities & Impact Upon their Physical and Mental Health." Global Pharmaceutical Sciences Review VIII, no. I (2023): 16-23. https://doi.org/10.31703/gpsr.2023(VIII-I).03
